Right to Work Benefits Fact Sheet Spring 2024 Summary
Download the Right to Work Benefits Fact Sheet Spring 2024 report.
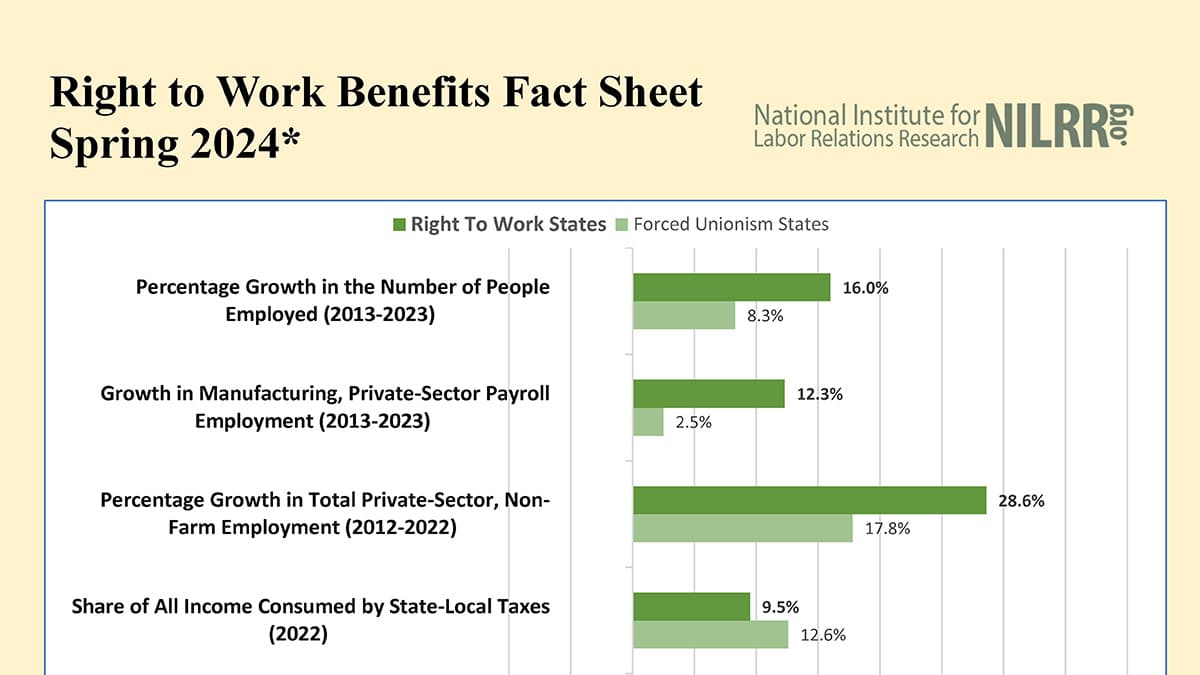
The Right to Work legislation, which allows workers to choose whether to join a union or pay union dues, has seen various changes across several states over the past decade. Michigan, which became a Right to Work state in 2013, repealed its law in March 2023, although it remained in effect until February 2024. Wisconsin (2015), West Virginia (2016), and Kentucky (2017) also adopted Right to Work laws. However, these states are excluded from multi-year analyses but are included in analyses since their laws took effect. Missouri’s Right to Work law, passed in 2017, was never enacted and thus is not recognized as a Right to Work state.
For detailed comparative economic data, inquiries can be directed to Stan Greer.
The data sources include employment growth figures from the Department of Labor’s Bureau of Labor Statistics, manufacturing and private-sector payroll growth from the BLS Establishment Survey, and private-sector non-farm employment growth from the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Economic Analysis. Other metrics include state-local tax burdens from the Tax Foundation, demographic shifts from the Bureau of Census (BOC), household consumption growth, cost of living-adjusted income from the Missouri Economic Research and Information Center, public pension plan liabilities, welfare recipient statistics, and housing authorizations, all providing a comprehensive view of the economic landscape in Right to Work states.
For further information, the National Institute for Labor Relations Research can be contacted at their Virginia address or by phone.

